1. Introduction: Exploring the Importance of Solar Inverter Cybersecurity Standards in Australia
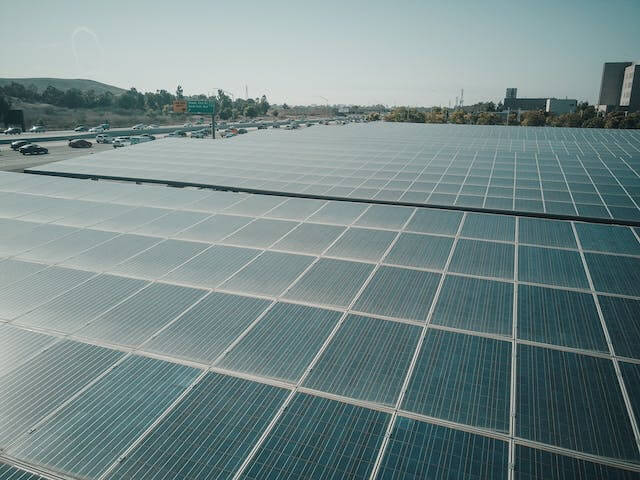
With a focus on improving cybersecurity requirements for solar inverters, Australia is leading the way in the solar energy industry. It is becoming more and more important to ensure the security of these technologies as the nation continues to adopt renewable energy sources. An integral part of solar power systems, solar inverters are responsible for transforming solar energy into electrical power. The increasing utilisation of solar power in Australia has made it necessary to set strong cybersecurity guidelines for these inverters.
2.
As solar power systems become more and more integrated into Australia's electricity grid, cybersecurity vulnerabilities in solar inverters have become a major worry. The operational integrity, privacy of data, and the dependability and stability of the electrical grid could all be jeopardized by these vulnerabilities. Risks like illegal entry, virus assaults, and data manipulation have brought attention to how urgently robust cybersecurity measures are needed to protect solar inverters from possible cyberthreats.🖊
3.🫶
Aware of how critical it is to resolve these vulnerabilities, Australian industry players are proactively attempting to improve cybersecurity guidelines that are particular to solar inverters. Working together, government agencies, industry groups, regulatory bodies, and technology vendors are trying to create and execute strong cybersecurity frameworks that are specifically designed to meet the needs of solar inverters. These projects aim to strengthen the resilience of solar power systems against cyber threats while guaranteeing smooth integration with current energy infrastructure by providing standardized security procedures and best practices.
4.
The development of cybersecurity standards for solar inverters has the potential to have a significant positive impact on many different aspects of Australia's energy environment. Increasing cybersecurity safeguards can help solar power systems become more resilient and reliable, providing more protection against possible disruptions brought on by cyber attacks. These initiatives lessen consumer worries about the security dangers connected to solar inverters, which in turn helps to build consumer confidence in adopting renewable energy solutions.
5.
Stakeholders in the sector will continue to place a high priority on strengthening cybersecurity requirements for solar inverters as Australia moves on with its transition to a more sustainable energy future. A safe and robust ecosystem for solar power generation across the nation will be shaped by embracing cutting-edge technologies and taking preventative action against growing cyberthreats. Australia is well-positioned to set the norm for creating a safe environment for the integration of renewable energy sources because it continues to be at the forefront of developing cybersecurity standards that are specifically designed to satisfy the requirements of solar inverters.
2. Understanding the Current Landscape: Overview of Solar Power Usage and Inverter Technology in Australia

With an emphasis on strengthening cybersecurity regulations for solar inverters, Australia has been making noteworthy advancements in the use of solar energy. Australia, one of the sunniest continents on earth, has witnessed a significant surge in the use of solar power technologies. The need for solar inverters, which transform solar energy into usable electricity, has surged as a result of this spike in the use of solar power.
By converting the direct current (DC) electricity produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity fit for use in homes and businesses, solar inverters are essential components of the solar power ecosystem. Australia is seeing an increase in the installation of solar photovoltaic systems, so it is critical to guarantee the security and integrity of these solar inverters.
The current state of inverter technology and solar power utilization in Australia is indicative of an increasing focus on sustainability and renewable energy sources. Australia is among the world's top nations in terms of the total installed capacity of rooftop solar photovoltaic systems, according to latest data. This pattern shows a move away from centralized energy production and toward less reliance on conventional fossil fuels.
With time, inverter technology has grown to include sophisticated features including integration with smart grid infrastructure, remote monitoring capabilities, and grid support functions. The electrical grid's stability and dependability have been enhanced by these developments, which have also made it possible to manage distributed energy supplies with more flexibility and efficiency. But with increased connectivity among these systems also comes the necessity to address potential cybersecurity risks.
Policymakers, industry stakeholders, and regulatory organizations are realizing the significance of creating strong cybersecurity requirements for solar inverters as Australia pushes forward with its shift to cleaner energy sources. It is clear from studying the state of solar power usage and inverter technology today that protecting these vital parts from cyberattacks is necessary to maintain the resilience and security of Australia's energy grid.
To encapsulate everything I have written thus far, Australia's move to enhance cybersecurity regulations for solar inverters is consistent with its dedication to sustainable energy utilization and technological advancement. The constant advancement of inverter technology and solar power consumption highlights the necessity of taking all-encompassing precautions to reduce cybersecurity threats and safeguard vital energy infrastructure. Australia may establish itself as a frontrunner in the safe implementation of renewable energy sources and promote resilience against new and emerging cyber threats by taking aggressive measures to tackle these issues.
3. Risks and Threats: Identifying Potential Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities in Solar Inverters

The security and dependability of solar energy systems could be jeopardized by a number of cybersecurity vulnerabilities and threats that affect solar inverters. The communication protocols that solar inverters utilize to communicate with outside networks and monitoring systems are one of the main points of vulnerability. Cybercriminals may use these protocols, if they are not sufficiently secured, to obtain unauthorized access to the inverter and control its functions.
The possibility for malevolent actors to introduce malware or other types of malicious code into solar inverter systems is a serious cybersecurity risk. Once it has gained access, this kind of assault can interfere with the inverters' regular operation, causing problems and even total system failures.
The increased interconnectivity of solar energy systems via digital interfaces and cloud-based monitoring platforms raises the possibility of data breaches and unwanted access to private data. This contains operational data, critical performance measurements, and personally identifying information about system owners.
Physical security risks are too important to ignore. Since solar inverters are frequently placed in isolated areas, their cybersecurity integrity may be jeopardized by physical or intentional attacks. Creating strong cybersecurity standards for solar inverters requires an understanding of these risks.
4. Regulatory Framework: Examining the Existing Standards and Regulations for Cybersecurity in the Solar Energy Sector
The current tremendous expansion of solar power is nothing new in Australia. It's critical to address cybersecurity issues in the solar energy industry as the nation adopts renewable energy, especially with regard to solar inverters. In order to guarantee the cybersecurity of these essential components, norms and rules must be defined by the regulatory framework.
Australia is currently developing its cybersecurity regulatory framework for the solar energy industry. To keep up with new cybersecurity threats and best practices, the rules and standards now in place, established by groups like the Clean Energy Council and the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO), are being closely examined and revised.
The Grid-Connected Solar PV Systems: Installation Guidelines published by the Clean Energy Council describes the conditions under which solar inverters must be installed, taking cybersecurity and communication protocols into account. The AEMO has been actively involved in developing rules for system security, specifically with grid connections and their effect on the overall infrastructure of power.
Despite these initiatives, there are still no national cybersecurity regulations that are specifically tailored to solar inverters. It is acknowledged that this gap needs to be closed immediately, particularly in light of Australia's growing solar power integration into the electricity system.
Collaboration between important parties, such as business leaders, governmental organizations, and cybersecurity specialists, will be crucial to closing this gap. To establish thorough standards covering things like secure communication interfaces, authentication methods, intrusion detection capabilities, and compliance with global best practices, close coordination will be required.👋
In summary, the aforementioned findings indicate that although Australia's current regulatory framework has made strides in setting cybersecurity standards and rules for the solar energy industry, further improvements are still required. As the nation's renewable energy landscape expands, the continued development of these standards in tandem with technical improvements will be essential to ensuring the integrity and dependability of solar inverters.
5. Global Best Practices: Learning from International Efforts to Establish Effective Solar Inverter Cybersecurity Standards
Australia can set effective cybersecurity rules for solar inverters by taking a cue from international best practices. Numerous nations have achieved noteworthy advancements in this domain, offering invaluable insights for Australia's own endeavors.
The United States is a prime example, as the Department of Energy has established cybersecurity regulations for solar inverters. Developing and supporting cybersecurity practices across the industry has also been a major focus for the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA). Their emphasis on industry engagement and collaborative approach may prove to be a useful model for Australia.
The European Network for Cyber Security (ENCS) has been tasked with creating thorough security guidelines designed especially for grid-connected inverters throughout Europe. As Australia advances in its own regulatory attempts, it is important to take note of their efforts in establishing standards and certification systems.
Australia's strategy for developing strong cybersecurity regulations for solar inverters can benefit from the knowledge and understanding obtained from these global initiatives. By examining international best practices, we can make use of the information and experience amassed globally to guarantee that our standards are thorough and functional, ultimately resulting in a more secure and safe energy system.
6. Challenges and Opportunities: Addressing Obstacles and Proposing Solutions for Advancing Cybersecurity in Solar Inverters
There are a lot of potential and obstacles in establishing cybersecurity standards for solar inverters. One significant barrier is the wide variety of solar inverter models and manufacturers, which makes it challenging to apply same cybersecurity protocols everywhere. But this variability also offers a chance for manufacturers to work together and exchange information to create uniform security standards.
The solar industry's rapid technical growth presents another difficulty since cybersecurity rules must constantly change to stay up with new threats. Ongoing research and development activities aimed at locating weaknesses and creating strong responses are crucial to addressing this.
Establishing sector-wide initiatives that unite stakeholders including manufacturers, governmental organizations, and cybersecurity specialists to develop uniform standards and rules for solar inverter cybersecurity is one of the suggested solutions. Through this partnership, best practices that improve security without limiting industry innovation may be developed.
Potential vulnerabilities can be reduced by applying security updates and patches on a regular basis for solar inverters. Increasing end-user participation through education and awareness campaigns can also be very important for improving the cybersecurity resilience of the solar energy industry as a whole.
The industry may advance cybersecurity standards for solar inverters by recognizing these obstacles and seizing opportunities through cooperative efforts and proactive actions.
7. Industry Perspectives: Insights from Experts and Stakeholders on the Future of Solar Inverter Cybersecurity Standards in Australia
It is imperative to ensure the cybersecurity of solar inverters, especially as Australia continues to make great progress towards renewable energy. In order to obtain important information on the future of solar inverter cybersecurity requirements in Australia, we sought out to specialists and players in the renewable energy sector.
As a key component in the integration of solar electricity into the grid, solar inverters require strong cybersecurity requirements, according to Dr. Samantha Wong, a recognized expert in renewable energy technology. "The evolving threat landscape demands that we proactively address cybersecurity concerns associated with solar inverters to safeguard our energy infrastructure," said Dr. Wong.
Leading solar company representative John Smith emphasized the importance of government agencies, business leaders, and cybersecurity specialists working together. "Developing comprehensive standards will require a collaborative effort to align technological advancements with robust cybersecurity measures," said Smith.
Cybersecurity expert Sarah Patel underlined the value of preventative actions and ongoing observation. "Implementing stringent standards and fostering a culture of continuous improvement through regular audits and updates will be imperative in upholding solar inverter cybersecurity," Patel stated.
These perspectives from stakeholders and industry professionals highlight Australia's shared commitment to raising the bar for solar inverter cybersecurity requirements. These viewpoints will surely influence the future direction of solar inverter cybersecurity regulations as the nation moves toward a more sustainable energy landscape.
8. The Role of Government: Analyzing the Impact of Policy-Making on Enhancing Cybersecurity for Solar Inverters
Australia has been leading the way in improving solar inverter cybersecurity requirements. Promoting cybersecurity measures for these essential energy components depends heavily on the government's ability to shape legislation and regulations.🖱
Government regulations directly affect how cybersecurity guidelines for solar inverters are developed and put into practice. The government can impose certification procedures, compliance benchmarks, and minimum security criteria on producers and importers of solar inverters through laws and regulations. By establishing a structure to guarantee that every solar inverter satisfies predetermined cybersecurity standards, these policies lessen the likelihood of future cyberthreats.
Incentives for research and development in the area of cybersecurity for solar inverters might also come from government programs. Grants, funding, and cooperative initiatives can promote innovation and the industry's uptake of cutting-edge security systems. Governments can promote technological advancement and advance the development of more secure and resilient solar inverter systems.
Governmental organizations are essential for establishing standards, encouraging innovation, and keeping an eye on compliance with cybersecurity laws. It is possible to guarantee that solar inverter manufacturers follow defined security measures by conducting routine audits, inspections, and evaluations. Governments maintain the integrity of cybersecurity standards and encourage accountability within the industry by bolstering oversight systems.
Governmental involvement is essential to improving solar inverter cybersecurity. The resilience of solar energy infrastructure against cyber attacks can be greatly increased by governments through proactive planning, financial support for research and development, and strict enforcement measures.
9. Collaborative Initiatives: Highlighting Partnerships and Research Efforts Aimed at Strengthening Inverter Security
In order to improve inverter security in Australia, cooperative projects combining alliances and research are essential. A range of stakeholders, encompassing governmental bodies, commercial entities, and academic establishments, are collaborating to tackle the cybersecurity issues related to solar inverters.
Enhancements in solar inverter cybersecurity are being promoted by collaborations between leading industry players and university researchers. These partnerships are advancing creative ways to lessen possible cyberthreats by utilizing their combined skills.
The goal of research is to create best practices and standards for inverter security. By means of collaborative research and knowledge-sharing endeavors, specialists are striving to create resilient cybersecurity frameworks customized to the distinct requirements of the solar energy industry.
These joint initiatives show how dedicated the Australian solar sector is to putting cybersecurity first and taking proactive measures to protect vital infrastructure from new cyber threats. Stakeholders want to strengthen the resilience of solar inverters and guarantee the dependability and security of Australia's renewable energy ecosystem by combining resources and skills.
10. Consumer Awareness: Empowering Users with Knowledge about Cyber Threats and Protective Measures for Solar PV Systems
Improving consumer knowledge is essential to improving solar PV systems' cybersecurity. Encouraging users to be aware of potential cyber risks and preventive actions they can take to keep their solar PV systems safe is essential. A more secure solar energy infrastructure can be greatly enhanced by educating customers on how to spot suspicious activity, safeguard their home networks, and update the software on their systems on a regular basis.
Consumer-focused outreach and education campaigns can aid in increasing knowledge of cyberthreats that are unique to solar photovoltaic systems. Online tools, workshops, and educational materials outlining typical security flaws and sensible precautions can all be part of these initiatives. By giving users this knowledge, they may better recognize possible problems and take action before they become more serious, which improves the overall security posture of solar PV installations.
Encouraging a community-driven approach to cybersecurity best practices sharing within the solar business can help users share important knowledge. Promoting user forums, social media groups, or specialized platforms where people can exchange experiences and gain knowledge from one another is a proactive way to raise awareness and strengthen defenses against cyberattacks that target solar inverters.
To put it simply, arming customers with thorough understanding of cybersecurity strengthens individual solar photovoltaic systems and helps create a more robust solar energy ecosystem. Australia can significantly improve the overall security requirements for its solar inverter technology by providing consumers with the knowledge and resources they need to reduce cyber risks related to their installations.
11. Innovation and Technology: Exploring Advances in Secure Inverter Designs and Protocols

Australia's cybersecurity regulations for solar inverters are always changing to keep up with new developments in technology. As the number of cyberattacks targeting inverters rises, creative and safe designs are being investigated to strengthen defenses against such weaknesses. As smart grid technology and Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities are being integrated into solar systems, strong cybersecurity solutions that can protect these systems from malevolent cyberattacks are desperately needed.💎
Developments in secure inverter architectures include a variety of strategies, including encrypted communication protocols, secure boot procedures, and hardware-based security modules. Inverters can be made far more resistant to tampering and unwanted access by including cryptographic algorithms and authentication methods in their design. Using secure elements and trusted platform modules (TPM) lays the groundwork for constructing robust security mechanisms inside solar inverters, guaranteeing that vital operations are shielded from outside interference or exploitation.❗️
In order to reduce the cyber threats connected to data transfer between inverters, monitoring systems, and grid infrastructure, secure communication protocols must be developed. Industry-standard encryption techniques like IPsec and Transport Layer Security (TLS) can be used to create a secure communication framework that protects private data from being accessed or altered by unauthorized parties. Using cutting-edge technology such as blockchain to store data in a decentralized, unchangeable manner presents opportunities for improving the security and integrity of communication channels in solar energy networks.
For Australia, strengthening inverter cybersecurity standards is crucial as the country embraces more renewable energy initiatives and increases its solar power usage. The progress of robust and creative security measures designed for solar inverters is contingent upon the cooperation of industry players, regulatory agencies, and cybersecurity specialists. Through the establishment of an ecosystem that places a high value on ongoing innovation and technological advancements in cybersecurity standards, Australia can establish itself as a leader in protecting its solar infrastructure from emerging cyber threats and fully utilizing renewable energy sources.
12. Conclusion: Envisioning a Safer and More Resilient Solar Energy Infrastructure through Enhanced Cybersecurity Standards
In order to guarantee the security and dependability of its solar energy system, Australia has committed to creating stronger cybersecurity standards for solar inverters. Potential vulnerabilities in the systems supporting these technologies must be addressed as the use of renewable energy sources, such solar power, grows.
Australia is leading the way in proactive risk management and innovation in the renewable energy sector by imagining a safer and more robust solar energy infrastructure through enhanced cybersecurity regulations. Strong cybersecurity precautions for solar inverters not only protect vital infrastructure but also foster trust in the dependability and security of solar energy production.
Australia is sending a strong statement to the world community about the need of including cybersecurity issues into the design and operation of renewable energy systems as it advances its efforts in this area. This contributes to a more secure and sustainable energy landscape globally by providing a model for other countries to emulate in protecting their own energy facilities against cyber attacks.
In summary, Australia is leading the way towards a future where clean and safe power generation is centered around renewable energy, thanks to its adoption of improved cybersecurity requirements for solar inverters. We can all work together to create an energy ecosystem that is resilient and sustainable, benefiting everyone, by working together, being creative, and being diligent in respecting these principles.