1. Introduction to the Australian Small-Scale Solar Industry
The small-scale solar market in Australia has expanded rapidly in recent years, and 2023 will be no different. The swift proliferation of small-scale solar installations on residential and commercial buildings can be attributed to the nation's ample sunshine and growing consciousness of environmental sustainability. Consequently, Australia has emerged as a global frontrunner in the domestic solar power market, propelling noteworthy transformations in the country's energy terrain. We will examine the most recent data and market trends affecting the Australian small-scale solar market in 2023 in this post.
2.📙
Australia is still seeing a sharp increase in small-scale solar installations in 2023. The Clean Energy Regulator reports that record numbers of small-scale solar systems, such as solar panels and solar batteries, have been installed. This pattern shows that Australian businesses and homeowners are moving more and more in the direction of sustainable and clean energy solutions. The adoption of small-scale solar systems across the nation has been further propelled by technological improvements and declining installation prices.
3.
Support and legislation from the government are essential to the development of Australia's small-scale solar sector. Numerous state and federal programs are still in place in 2023 to encourage people and businesses to participate in solar power generating. These include initiatives like feed-in tariffs, incentives, rebates, and net metering plans that work to increase consumer access to and affordability of renewable energy. As Australia moves toward a sustainable energy transition, the importance of small-scale solar has been emphasized by ongoing policy promises to cut carbon emissions.
4.
The widespread use of small-scale solar power systems has resulted in favorable socio-economic outcomes for both private residences and the larger community. It not only gives homeowners more control over how much energy they use and how much they pay for it, but it also generates jobs in the renewable energy industry. A greater amount of clean energy produced locally helps to lessen dependency on conventional fossil fuels, which encourages energy independence and improves environmental stewardship.
5.
Even with its impressive expansion, the Australian small-scale solar market still has several issues that need to be addressed. These include continuing market competitiveness, regulatory complexity, and grid integration challenges. Nonetheless, these obstacles also offer chances for creativity and cooperation within the industry. There is tremendous opportunity for more small-scale solar capacity optimization as energy storage solutions like household battery systems gain popularity.
6.
With 2023 and beyond in sight, Australia's small-scale solar sector has a bright future. It is anticipated that further technological developments will reduce installation costs and increase system effectiveness. The smooth integration of distributed solar generation into the current infrastructure will be made possible by the integration of smart grid systems. Growing consumer interest in clean energy solutions is anticipated to be a result of a greater emphasis on sustainable development, which will accelerate the expansion of small-scale solar systems throughout Australia.
In conclusion...
In 2023, the Australian small-scale solar market is poised for growth and offers a plethora of opportunities. The outlook for additional growth is excellent given the combination of strong government support systems and changing consumer tastes that favor sustainable options.
2. Overview of Solar Energy Trends in Australia
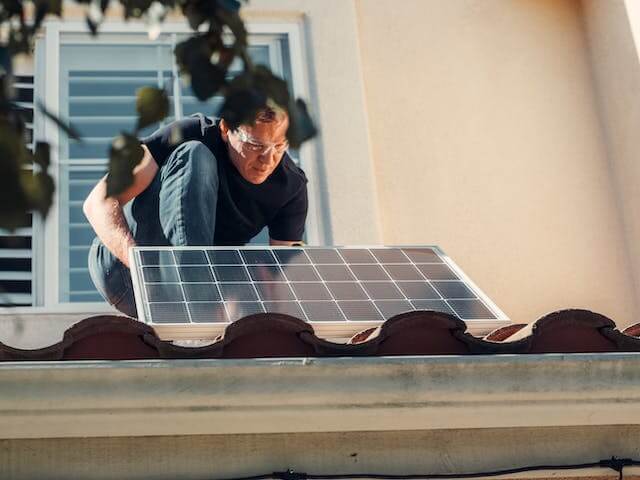

Australia has seen a notable increase in the number of small-scale solar energy installations in recent years. The movement has been largely fueled by the nation's plentiful sunshine and encouraging policies from the government. Small-scale solar power system adoption has been welcomed by Australians, who are placing more emphasis on sustainability and renewable energy sources.🔹
Rooftop solar panel installations are becoming increasingly common on both residential and commercial premises as a result of the move towards renewable energy alternatives. This pattern indicates a desire to lessen carbon footprints and an increasing knowledge of environmental challenges. The popularity of solar technology has been further fueled by its falling cost, which has made it more accessible to a larger spectrum of users.
Technological developments in battery storage have coincided with the expansion of small-scale solar power systems. With the ability to store solar energy for later use, homeowners and businesses may now increase the overall efficiency and dependability of their solar power systems. Because of this, integrating solar battery storage solutions has spread throughout Australia as a regular practice.
Australia's small-scale solar energy installations are growing, which indicates a positive trend towards more ecologically friendly and sustainable power production. This pattern is probably going to continue as the country works to become less dependent on conventional fossil fuels and become more energy independent.
3. Key Statistics on Small-Scale Solar Installations in 2023
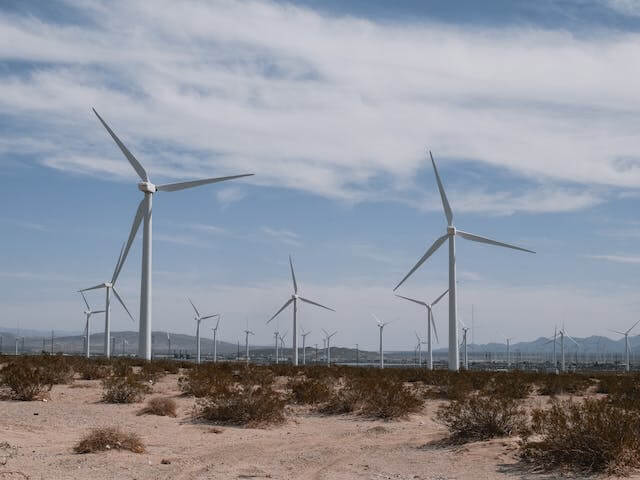

Australia's small-scale solar arrays are thriving in 2023 and making a substantial contribution to the nation's renewable energy targets. The important figures pertaining to small-scale solar installations demonstrate the expansion and significance of this sector. Australia is expected to have more than 2.66 million rooftop solar systems by 2023, with a capacity of more than 15 gigawatts (GW). This is a significant rise over prior years and demonstrates how widely solar electricity is being used by both residential and commercial customers.
According to the data, small-scale solar systems make for about 23 percent of Australia's total capacity for producing electricity. This illustrates how important small-scale solar is to diversifying the nation's energy sources and lowering its dependency on fossil fuels. Notably, states like Victoria, New South Wales, and Queensland have become leaders in the country when it comes to small-scale solar deployment, which is indicative of a national trend toward decentralized energy generation.
According to the data, small-scale solar installations are becoming more and more of an economical choice for Australian homes and companies. Compared to ten years ago, the average cost per watt has decreased by almost 50%, demonstrating the financial benefits of investing in solar technology. Costs have been falling, which has accelerated small-scale solar's adoption and accessibility and brought it into the mainstream energy market.
These important figures paint a vivid picture of Australia's small-scale solar industry in 2023, one that is distinguished by quick growth, increased capacity, leadership in the region, and affordability. With such optimistic numbers guiding the industry's course, Australia's sustainable energy future is expected to heavily rely on small-scale solar power.
4. Factors Driving Growth in Small-Scale Solar Adoption
Australia's small-scale solar adoption is increasing due to a number of important factors. The fact that solar technology is becoming more and more accessible and inexpensive for businesses and homeowners is one important element. The popularity of small-scale solar systems has also been fueled by the desire for energy independence and a growing awareness of environmental responsibility.
Policies and incentives from the government are essential for encouraging the expansion of small-scale solar adoption. Feed-in tariffs, rebates, and subsidies are a few examples of programs that encourage people and businesses to engage in solar technology by offering favorable terms and financial support for solar installations. By lowering the initial costs of installing solar panels, these incentives promote the use of renewable energy sources among a larger number of individuals.
The rise in small-scale solar usage can also be attributed to technological advancements in the solar industry. Efficiency gains, increased storage capacity, and connection with smart home systems have increased the allure of solar electricity for customers. People can now embrace small-scale solar without having to make a large upfront investment more easily thanks to favorable financing options including power purchase agreements and solar leasing.
The need for small-scale solar installations has surged as a result of enterprises' increasing inclination towards sustainable practices and corporate social responsibility. Businesses are realizing the advantages of using renewable energy sources, such as solar power, to save energy costs and lessen their carbon footprint. It is anticipated that this tendency will accelerate the use of small-scale solar in a number of industries.
Some of the main causes propelling Australia's small-scale solar adoption boom are falling costs, encouraging government regulations, technology breakthroughs, attractive financing alternatives, and rising sustainability-related demand. As 2023 and beyond approach, these variables are expected to continue influencing the adoption of renewable energy in the nation.
5. Challenges and Barriers for Small-Scale Solar in Australia
To ensure the sustained prosperity of small-scale solar in Australia, it is imperative to tackle the prevailing obstacles and difficulties. The initial expense associated with installing solar panels is one of the primary obstacles. The initial investment can still be a barrier for many people and enterprises, even in the case of declining pricing. For certain prospective solar consumers, obtaining reasonably priced financing alternatives continues to be a difficulty.
The intricacy and inconsistent application of regulations in various states and territories is another major obstacle. This leads to misunderstandings and increases the administrative workload for installers and customers alike. Reducing restrictions and offering more precise instructions may assist in mitigating this barrier to the general use of small-scale solar power.
Problems with grid connections arise because the current electrical infrastructure is being overloaded by the growing number of small-scale solar installations. Technical issues like voltage swings and reverse power flows may result from this. Investing in smart energy management technologies and grid upgrading will be necessary to address these issues.
It is essential to inform customers about the advantages of small-scale solar power and to debunk any rumors or false beliefs about its dependability and cost. It is possible to dispel any doubt or false information that would discourage people from making a solar energy investment by giving factual information about potential savings, environmental impact, and technology improvements.
Last but not least, fostering equity in the adoption of renewable energy requires providing sufficient assistance for low-income households or renters who can encounter extra obstacles in gaining access to small-scale solar solutions. Closing the gap and increasing access to solar energy for all Australians can be achieved by the implementation of policies or incentives designed especially for these groups.
6. Case Studies: Successful Small-Scale Solar Projects in Australia
In recent years, Australia has witnessed a number of successful small-scale solar projects that demonstrate the potential and advantages of using solar energy. The Kidston Solar Project in Queensland, developed by Genex Power, is one notable case study. This ground-breaking project showcases the combination of sophisticated energy storage technologies and solar power with a 50-megawatt (MW) solar farm and a 250-MW pumped hydro storage facility. In addition to increasing the amount of renewable energy produced in the area, the project has given important information about the viability and efficiency of large-scale solar projects.🤍
Goldwind Australia's White Rock Solar Farm in New South Wales is another outstanding example. With a 175MW capacity, this project has helped the state meet its renewable energy goals and stimulated regional economic development. The feasibility and scalability of small-scale solar initiatives throughout Australia are demonstrated by the successful installation and operation of such large-scale solar farms.
On a lesser scale, community-based initiatives such as RAW Energy (Renewable Albury-Wodonga Energy) have acquired popularity due to their significant contributions to regional sustainability campaigns. The focus that RAW Energy places on rooftop solar installations and community involvement is an example of how grassroots efforts can promote the widespread adoption of small-scale solar solutions locally.
Together, these case studies show the variety of strategies and successful results connected with small-scale solar installations around Australia. They confirm Australia's leadership in advancing the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy landscape and act as motivating role models for stakeholders looking to use renewable energy technology for sustainable development.🥳
7. Government Policies and Incentives for Small-Scale Solar
Through a number of initiatives and policies, the Australian government is still encouraging the use of small-scale solar systems in 2023. One of the main forces for the nation's continued support for small-scale solar systems is the Renewable Energy Target (RET). By 2020, the RET seeks to guarantee that 33,000 gigawatt-hours or more of Australia's electricity are generated from renewable sources, with a particular share going toward small-scale solar power plants.
Property owners and tenants who install qualifying small-scale renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, can receive financial incentives from the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES). Small-scale technology certificates (STCs), which can be exchanged or sold to recover a portion of the system's cost, are made for these installations under this plan. In Australia, the SRES is still very important in promoting the use of small-scale solar energy as of 2023.
To encourage the adoption of solar power on a modest scale, a number of state and territory governments provide their own subsidies and incentives. These programs, which aim to increase the affordability and accessibility of solar electricity for homes, businesses, and community organizations, may involve subsidies, feed-in tariffs, or low-interest loans. States such as Queensland and South Australia, for example, have put in place specialized initiatives designed to encourage the installation of small-scale renewable energy systems within their borders.✨️
The Australian government also funds research and development projects in small-scale solar technologies and collaborates with industry stakeholders on these projects. Policymakers hope to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and broaden the possibilities of small-scale solar solutions while hastening their adoption in the residential and commercial sectors by funding research and advancement in this field.
Australia's small-scale solar market is mostly shaped by government policy and incentives. By taking these steps, renewable energy becomes more financially appealing while simultaneously lowering greenhouse gas emissions and improving local energy security. Maintaining the momentum behind small-scale solar adoption across the country will be crucial as we go into 2023 and beyond, with the cooperation of policymakers.
8. The Future Outlook of Small-Scale Solar in the Australian Energy Market

As we approach 2023, the Australian energy market's prospects for small-scale solar appear bright. The small-scale solar industry is expected to increase significantly due to ongoing technological advancements, falling solar panel costs, and rising environmental awareness.
The Australian government has demonstrated a strong commitment to renewable energy programs in recent years, offering financial incentives to individuals and companies looking to invest in solar power. It is anticipated that nationwide adoption rates of small-scale solar systems will continue to be fueled by this support.
Small-scale solar power is one of the sustainable energy alternatives that are in greater demand as customers become more aware of their environmental impact and want to use less traditional fossil fuels. The prospects for Australia's small-scale solar business are further being enhanced by this shift towards sustainable energy choices.
Small-scale solar installations are becoming more feasible because to developments in battery storage technology, which allow users to store extra energy produced during peak solar hours for use during low- or no-sun times. Small-scale solar systems are now more dependable and efficient thanks to this advancement, which increases their allure for energy users.
In summary, the future of small-scale solar in the Australian energy industry seems promising due to sustained government support, growing environmental awareness, and technology breakthroughs boosting price and efficiency. Looking ahead to 2023 and beyond, we can expect small-scale solar solutions to continue growing and being widely adopted across Australia.