1. Introduction to Peter Dutton's home battery claim
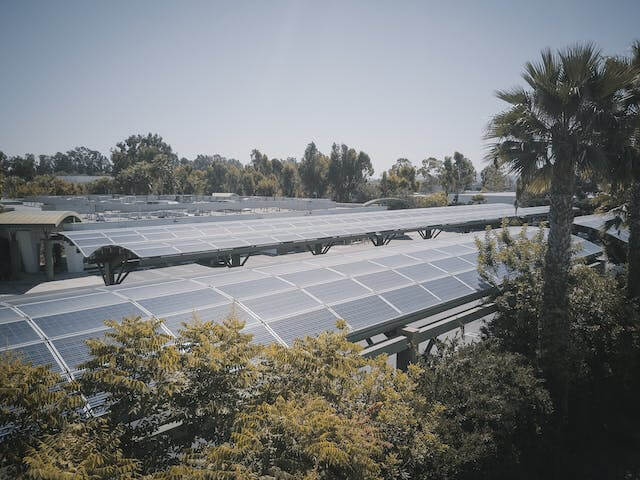
Australian Minister for Defence Peter Dutton recently made a bold assertion regarding home battery systems and how they can save electricity bills. According to Dutton, installing batteries in a home may result in a 60% reduction in electricity costs. Although homeowners facing increased energy bills may find this claim alluring, energy sector professionals have expressed concern about it. Let us analyze Dutton's argument more closely to see if it is genuinely "half-baked," as some opponents have indicated, or if it actually makes sense.
2.
To put it mildly, Dutton's claim that residential battery systems may result in a 60% reduction in electricity costs is somewhat ambitious. Many in the energy industry have questioned this claim's validity, pointing to a number of potential limiting issues. For example, a variety of factors, including household energy usage habits, solar panel efficiency, local electricity rates, and battery system costs, affect the actual savings from installing home batteries. How well customers control their energy use and optimize the returns on their investment may also have an impact on how successfully house batteries balance electricity expenditures.
3.📱
Dutton's assertion has been discussed by analysts and industry specialists, who have offered opinions that differ from his sanguine appraisal. While house batteries can undoubtedly help lower electricity costs, some contend that a 60% overall reduction in costs is unduly ambitious and unaccountably unrealistic. They underline that before making broad claims about possible cost reductions, a comprehensive assessment that takes into account unique situations and market factors is necessary.
4.
One main takeaway from discussions on Dutton's claim's veracity is that consumers ought to evaluate statements regarding home batteries critically and cautiously. Homeowners should carefully assess their individual energy usage patterns and long-term financial ramifications, seek guidance from reliable experts or installers, and undertake in-depth study before considering the installation of home battery systems.
5.
The debate surrounding Peter Dutton's claim is still developing, but it's becoming obvious that any general guarantee of a 60% reduction in electricity costs via home battery installation is cause for serious doubt. Although there is no denying that home batteries have the potential to lower energy bills for some homes, realistic expectations must be set. While considering their options for incorporating house battery systems into their energy infrastructure, consumers must obtain thorough information and make informed decisions.
2. The potential impact of home batteries on energy use
Experts and proponents of renewable energy expressed suspicion towards Peter Dutton's recent assertion that a toaster could not be powered for an hour by household batteries. Opinions regarding the possible influence of household batteries on energy consumption are becoming more and more prevalent as the Australian government continues to encourage fossil fuels.
Because they store extra solar or grid energy for later use, home batteries have the potential to completely transform how people utilize energy. This may lessen the reliance on conventional energy sources during periods of high demand, relieving pressure on the grid and fostering the development of a more sustainable energy environment. Increased homeowner and community self-sufficiency as well as lower overall energy expenditures could result from the widespread use of home batteries.
The stability and dependability of the grid could be improved by home batteries. Home batteries can lessen the burden on the grid by allowing customers to store excess energy during off-peak hours and use it during periods of high demand. This lowers the possibility of blackouts or power shortages during periods of heavy demand, which eventually helps the general electrical infrastructure as well as individual customers.
The environmental effects of home battery adoption are equally important. Home battery systems help to lessen dependency on fossil fuels and carbon emissions by enabling homes to store and use renewable energy when necessary. This is in line with international initiatives to combat climate change by encouraging the use of cleaner, more sustainable energy sources.
Home batteries have a significant potential influence on energy use. Home batteries present a viable way to update our perspective on energy use, from relieving pressure on conventional energy sources and improving grid stability to promoting more environmental sustainability. Even though some have questioned their efficacy, continuous developments in battery technology along with growing public support show that batteries have a lot of potential to influence our future energy environment in a way that is more sustainable, dependable, and efficient.
3. Exploring the feasibility of Dutton's claim
Examining the viability of Peter Dutton's assertion about house batteries is essential to determining the usefulness and possible consequences of this kind of plan. Although home batteries have drawn interest as a potentially useful technology for storing electricity produced from renewable sources, there are a number of practical issues that need to be addressed before they can be widely implemented across the country.
The cost-effectiveness of installing home batteries throughout households is one thing to look into. Although supporters claim that it may result in long-term energy bill savings and less dependency on the grid, many households may find the initial cost of buying and installing these systems to be a substantial financial obstacle. When considering whether house batteries are feasible, it's important to consider the upkeep and replacement costs associated with them over time.
The ability of the current infrastructure to enable the widespread adoption of house batteries is a crucial component in determining the viability of the project. This involves things like making sure that the system is compatible with the grid, taking care of any technical issues that may arise from combining multiple decentralized battery systems, and putting in place legal structures to control excess energy production locally.
Examining the viability of Dutton's assertion also requires taking the environment into account. This includes an evaluation of the lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions linked to the production of batteries and the procedures for managing old battery units once they reach the end of their useful lives. Determining house batteries' practicality as a component of Australia's energy transition strategy requires an understanding of how they fit into larger sustainability objectives.
Taking into account everything mentioned above, we can say that although house batteries have the potential to improve distributed energy storage and lessen dependency on conventional power infrastructure, more research must be done to determine their viability before adopting them as a national solution. Crucial elements in evaluating whether Peter Dutton's plan for the broad adoption of house batteries is feasible in reality include addressing economic problems, evaluating infrastructure readiness, and taking environmental factors into account.
4. Comparing home battery technology with traditional energy sources
It is critical to assess Peter Dutton's latest assertion regarding home batteries by contrasting this new technology with conventional energy sources. By enabling homeowners to store extra solar energy for later use, house battery systems mark a move toward decentralized energy storage. By contrast, conventional energy sources like natural gas and coal depend on large-scale power facilities with extensive transmission and distribution networks.
When considering home battery technology in comparison to other energy sources, flexibility and resilience are advantages. When demand is at its highest, households can reduce their reliance on the grid by having the capacity to store excess energy. This can lessen the burden on the infrastructure supporting centralized power and lessen the likelihood of blackouts during severe weather or other disturbances. Conventional energy sources, on the other hand, are more susceptible to disruptions in the fuel supply chain and changes in fuel pricing.
In terms of environmental impact, house battery technology outperforms conventional energy sources hands-down. Homeowners can drastically lessen their dependency on fossil fuels for the production of electricity by employing stored solar energy. By doing this, greenhouse gas emissions are decreased and a more sustainable energy future is facilitated. On the other hand, conventional energy sources like coal and natural gas play a big role in the pollution of the air, water, and climate due to carbon emissions.
One essential thing to think about is how much house battery technology is going to cost in comparison to other energy sources. A house battery system can save money over time by lowering dependency on the grid for electricity, particularly during peak rate periods, even though the initial cost may be high. Conventional energy sources frequently entail unpredictable fuel prices as well as continuous maintenance expenditures related to the infrastructure and operations of power plants.
All of the above leads us to the conclusion that house batteries offer several benefits in terms of flexibility, resilience, environmental impact, and cost-effectiveness when compared to traditional energy sources. Residential energy storage offers a viable substitute for reliance on centralized power supply from conventional sources as the market for it grows and develops.
5. Assessing the environmental benefits and drawbacks of home batteries
Evaluating house batteries' advantages and disadvantages with regard to the environment is essential to comprehending the total effect of this technology. On the one hand, by storing extra solar power for later use, household batteries can minimize carbon emissions and lessen dependency on non-renewable energy sources. This can lessen the effects of climate change and help create a more sustainable energy system. If household batteries are widely used, there may be less stress on the electrical grid during peak hours, which would encourage more energy-efficient use.
There are, however, disadvantages to take into account. Environmental expenses associated with battery system development and disposal include resource extraction, industrial emissions, and waste management. Although household batteries can lessen a person's dependency on the grid, they may also cause the energy system to become more fragmented if they are not effectively handled on a broader scale.
It is crucial to evaluate these advantages and disadvantages holistically, taking into account things like the battery's lifespan, the source of electricity used to charge it, and the system's total contribution to lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Making judgments regarding the integration of house batteries into our energy grid requires a thorough understanding of these intricacies.
6. Investigating the economic implications of widespread home battery adoption
Examining the financial effects of widespread adoption of home batteries involves a wide range of intricate considerations. It's critical to examine the possible economic impact of house battery installations, as Peter Dutton's recent remarks generated discussion over their practicality. The possible decrease in reliance on conventional electricity grids is one important factor. The widespread adoption of home batteries by families might potentially reduce the burden on the nation's infrastructures and result in long-term financial benefits for energy providers as well as customers.
A growing market for renewable energy technology could result from the widespread use of residential batteries. Because of economies of scale, this might reduce manufacturing costs and increase the accessibility of sustainable energy solutions for a wider range of people. The renewable energy sector may experience a rise in job creation as technology evolves and becomes more widely used, offering new chances for innovation and employment.👍
There are bigger macroeconomic consequences that need consideration. Deploying household batteries on a broad scale could potentially cut greenhouse gas emissions and alleviate the effects of climate change if it results in less demand for fossil fuels, especially during peak hours. These environmental advantages can lessen the financial constraints connected to environmental deterioration by having a domino effect on public health and the stability of the infrastructure.
We can infer from all of the foregoing that there are intricate interactions between consumer behavior, market dynamics, environmental effects, and technology advancement when analyzing the economic implications of widespread adoption of home batteries. Even though there are still many unknowns and difficulties, investigating these ramifications might offer insightful information about how adopting this technology might change the way we use energy and improve society more broadly.
7. Considering the challenges and obstacles to Dutton's proposal
The usage of household batteries by Peter Dutton as a possible remedy for Australia's energy dilemma is beset with a number of serious problems. The practicality and cost of putting this technique into practice on a large basis are two big obstacles. Home battery installation and purchase can be expensive up front for a lot of houses, which keeps them from being widely used.
The requirement for significant infrastructure modifications in order to support a grid powered by household batteries presents another challenge. The energy from distributed battery systems may be too much for the current grid infrastructure to handle, necessitating careful planning and large investment to guarantee a seamless transition.
The effects of manufacturing and disposing of household batteries in large quantities on the environment are a concern. There are concerns regarding Dutton's proposal's overall sustainability because the manufacture process and disposal of these batteries could harm the environment if not handled appropriately.
Another problem is guaranteeing the security and dependability of a system that depends on dispersed home batteries. An overall energy supply that is susceptible to disruptions and security vulnerabilities is not one that can be prevented by putting strong processes in place to manage and maintain these discrete systems.
It will be necessary to do extensive planning, work with industry stakeholders, and possibly reconsider some parts of Dutton's idea in order to overcome these obstacles and guarantee the program's long-term viability as an energy option for Australia.
8. Examining public opinions and reactions to the claim
A variety of responses have been elicited by analyzing popular perceptions and reactions to Peter Dutton's home battery accusation. A number of people have voiced doubts on the claim's viability, raising issues with its usefulness and economics. The possible effects on households, especially those with low incomes, have drawn criticism from some.
Experts in renewable energy and environmental advocacy have stressed the importance of doing a thorough review of the plan. The significance of taking into account long-term advantages of alternative sustainable energy options has been emphasized.
On the other hand, proponents of the assertion have applauded it as a move in the direction of encouraging eco-friendly household actions. They see it as a chance to cut carbon emissions and make a positive impact on the environment.
The public's response to Peter Dutton's home battery claim highlights the need for careful consideration and deliberation prior to enacting such laws. The differing points of view are indicative of a continuing conversation about sustainable energy decisions and their broader consequences.
9. Analyzing potential government initiatives for promoting home battery usage
A household's ability to obtain and finance these sustainable energy solutions should be the first priority when thinking about possible government programs aimed at encouraging the use of home batteries. One method to encourage homeowners to invest in house battery systems and incorporate them into their renewable energy setups could be to offer subsidies or tax benefits. Developing awareness-raising and adoption-promoting educational initiatives and informational campaigns regarding the advantages of home batteries could be helpful.
Simplifying regulatory procedures and standards for home battery installation can also lower barriers to entry, making it easier for consumers to adopt this technology. By assessing these potential initiatives and adopting a proactive stance to promote home battery usage, the government can play a crucial role in advancing sustainable energy practices at the household level. The government could also look into partnering with energy companies to offer discounted installation services or financing options for homeowners interested in incorporating home batteries.
In summary, strategic policy implementation, financial incentives, instructional resource provision, and process simplification are critical components that might significantly influence the general adoption of house batteries. Governments may empower households to take control of their energy consumption and help create a more sustainable future by implementing these measures.
10. Discussing alternative solutions for sustainable energy use
To prevent climate change and lessen dependency on conventional power sources, a range of alternative solutions related to sustainable energy use might be investigated. The extensive use of solar panels in conjunction with residential battery storage systems is one such alternative. Because these systems store extra energy produced during the day for use at night or during periods of peak demand, they have the potential to considerably reduce carbon emissions. 🥸
The creation of cutting-edge grid infrastructure is an additional option for sustainable energy consumption. Energy distribution and consumption may be more effectively managed by smart grids using automation and sensor technologies, making it possible to utilise renewable energy sources like solar and wind power more effectively. A more sustainable energy future may be made possible by smart grid technology, which maximizes electricity flow and reduces waste.
Moving toward sustainable energy consumption requires funding research and development of next-generation clean energy technology. This covers developments in geothermal energy, hydrogen fuel cells, offshore wind farms, and energy storage. We can increase our capacity for renewable energy while lowering our impact on the environment by consistently developing and improving these technologies.
Another important alternative strategy for sustainable energy use is to promote energy efficiency in all sectors, from industrial to household. Stricter building rules, energy-efficient appliance incentives, and the promotion of environmentally friendly behaviors can all help to dramatically reduce overall energy usage and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
Sustainable energy consumption can also be enhanced by implementing decentralized microgrids, which enable communities to produce and distribute their own renewable electricity locally, in addition to these options. These microgrids reduce transmission losses, increase resilience to outages, and provide communities the tools they need to effectively manage their energy resources.
A multidisciplinary approach that incorporates policy interventions, public awareness campaigns, technological advancements, and industry collaboration is necessary to explore alternative solutions for sustainable energy use. By embracing a variety of strategies aimed at minimizing environmental impact while meeting growing energy demands, we can work towards building a cleaner and more sustainable future.
It's evident that there are several approaches to achieve sustainable energy consumption, ranging from improving storage choices like household batteries to utilizing renewable energy sources like solar power and developing grid infrastructure. While meeting society's increasing demand for electricity, each contributes in some way to the reduction of carbon emissions.
11. Concluding thoughts on Peter Dutton's half-baked home battery claim
After putting everything above together, we can say that Peter Dutton's claim that house batteries are too expensive and impracticable is out of step with the advancements being made in renewable energy technology. The potential of house batteries to help the grid and their declining cost point to a bright future for this technology. The increasing use of solar power and battery storage systems by households is expected to spur additional developments and cost reductions in these solutions due to the increased demand. Legislators must encourage the integration of sustainable energy technology into residences and commercial buildings and acknowledge the rapidly changing nature of this field. Neglecting the potential of household batteries could impede Australia's efforts to develop a more resilient and sustainable energy system. As a result, it is critical to evaluate this technology using data and trends from the present rather than stale assumptions.