1. Introduction to the idea that big things take time, followed by an exploration of the rapid growth of solar farms as a modern development marvel.
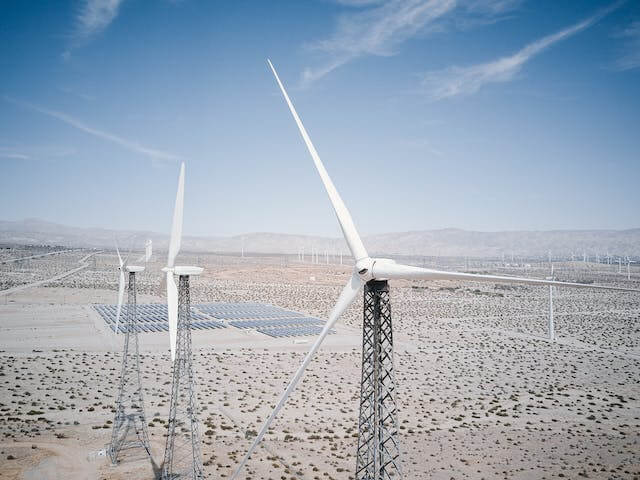
Large-scale initiatives can now be finished more quickly than ever before, even though big successes frequently require time. This is because technology is advancing so quickly. The quick expansion of solar farms across the globe is one such miracle. Even though Rome wasn't constructed in a day, the rate at which these contemporary buildings are being created is astounding and is revolutionizing the way that we use renewable energy.
Solar farms have become a symbol of environmentally conscious development and sustainability in recent years. Their quick growth is a proof of the global community's resolve to move away from fossil fuels and toward greener energy sources. The growth and spread of solar farms has shown how committed mankind is to addressing climate change and how quickly large-scale renewable energy infrastructure can be put into place.
This blog article will examine the incredible speed at which solar farms are being built, as well as how streamlined procedures and technical developments have made these massive projects possible. We'll look at what's causing this acceleration and discuss how such rapid advancements may affect the world's shift to renewable energy.
2. Delve into the complexities and challenges involved in constructing ancient Rome, juxtaposed against the efficient process of building a solar farm.
Building ancient Rome was an enormous undertaking that required careful planning, a lot of labor, and many difficulties. Coordination between engineers, architects, and laborers was crucial for the city's infrastructural development. It took years or perhaps decades to build the Colosseum and other magnificent monuments because they required precise engineering and craftsmanship.🥃
On the other hand, building a solar farm is an example of efficiency and speed. Solar farms may be built in a comparatively short amount of time thanks to technological developments and efficient construction methods. Utilizing contemporary building methods, the installation of solar panels, electrical systems, and associated infrastructure is a well-organized process that shortens the project's duration.
While the construction of ancient Rome faced many different challenges, such as where to find materials for massive structures like marble or how to get around logistically when moving heavy stones over long distances, the challenges associated with the construction of solar farms are mainly land acquisition, permitting, and grid connections, which are handled by careful planning and following regulations.
While the architectural wonders of ancient Rome serve as timeless examples of human skill and tenacity, the quick installation of solar farms represents our capacity to modify contemporary technologies for environmentally friendly energy sources. From intricate prehistoric buildings to effective renewable energy initiatives, humankind has progressed toward adopting novel approaches to meet changing societal demands.
3. Discuss the historical context of Rome and its enduring legacy, then transition into the potential long-term impact of solar farms on sustainability and energy independence.
The "Eternal City," Rome, is renowned for its magnificent architecture and long legacy. It has played a significant role in history. The Colosseum and aqueducts are two remarkable examples of the advanced construction techniques used by the ancient Romans. This historical background emphasizes Rome's value as a long-lasting and innovative emblem.
Moving from the historical background of Rome to the urgent global concerns of today, energy independence and sustainability are the main topics of conversation. Similar to the construction of Rome, the shift to sustainable energy sources has been a gradual process. But as technology has advanced, the emergence of solar farms offers a viable long-term sustainable alternative. By reducing dependency on non-renewable energy sources, these solar farms could open the door to greater energy independence.
Adopting solar energy promotes innovation and opens the door to a more sustainable future, which is in line with Rome's lasting heritage. Beyond only being good for the environment, solar farms also help to reduce carbon emissions and slow down climate change over the long run. Expanding the use of solar energy can increase energy independence, lessen dependency on limited resources, and foster stability in the economy.
Taking into account everything mentioned above, we can say that the historical background of Rome provides motivation for valuing longevity and creativity. Making the switch to solar farms reflects this philosophy by providing a route toward sustainable energy solutions that have a significant impact on energy independence and global sustainability. Like Rome is a monument to human perseverance and invention, solar farms have the ability to leave a long-lasting legacy of environmental care for coming generations.😺
4. Highlight notable achievements and engineering marvels from ancient Rome, drawing parallels to the innovative technology and design principles used in creating efficient solar farms today.
Many of the amazing engineering achievements of ancient Rome have lasted the test of time. Roman aqueducts, like the Pont du Gard in France, are considered engineering marvels of antiquity. These constructions used a precise gradient to move water over great distances while maintaining a constant flow. In a similar vein, modern solar farms use state-of-the-art engineering and technology to effectively catch solar radiation and transform it into electrical power.
Roman engineering is further demonstrated by the magnificent Colosseum. This amphitheater demonstrated cutting-edge building techniques and could hold tens of thousands of people thanks to its creative use of arches and vaults. Modern solar farms increase energy production by careful planning and layout, following a similar spirit of innovation. Carefully positioning the solar panels maximizes their exposure to sunshine and guarantees effective energy production.
Another enduring example of ancient engineering prowess is the Roman highways. Trade and transportation throughout the Roman Empire were made easier by the network of roadways they constructed. In the current pursuit of sustainable energy solutions, networked solar farms are essential for distributing clean electricity between different locations. Solar farms are linked together to create a vast grid that disperses renewable energy throughout large areas, much like Roman highways did when they connected far-flung cities.
One of the most amazing construction projects in all of ancient Rome is the Pantheon. Even after almost two millennia of construction, its enormous concrete dome continues to be the largest unreinforced concrete dome in the world. This long-lasting building provides an example of the durability and longevity that contemporary solar farms strive for. Modern solar farms are constructed using robust design concepts and long-lasting materials to endure severe weather conditions and continuously provide clean electricity for many years.
The engineering feats of ancient Rome, ranging from aqueducts to amphitheaters, never cease to amaze us. Similar to this, the creation of effective solar farms is a reflection of our dedication to using cutting-edge science and design concepts to create a sustainable future. Finding similarities between these two periods of human history allows us to acknowledge the long-lasting influence of innovative engineering techniques.
5. Explore the individual roles of various components that made up ancient Rome's grandeur and compare it to the different elements involved in setting up a functional solar farm.
The greatness of ancient Rome was based on a number of essential elements, including its complex road system, its superior architectural achievements, and its effective water management via aqueducts. These components worked together to make Rome a powerful icon and a successful metropolis.
In a similar vein, assembling a working solar farm requires a number of crucial parts. The main components that absorb sunlight and transform it into electrical energy are solar panels. In order to transform the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) for usage in electrical networks, inverters are essential. Transformers aid in controlling voltage levels, and mounting structures guarantee the best possible light exposure and support for the solar panels. Finally, the delivery of solar-generated electricity to end customers is made possible via the electrical grid connection.
Modern technology and sustainable energy practices are essential for a functioning solar farm in order to capture the sun's power for electricity generation, whereas the architectural marvels and infrastructure of ancient Rome were necessary for the city's grandeur. Rome's historical accomplishments and contemporary solar farms both serve as examples of how combining different elements can result in long-lasting advances for civilization.
6. Examine the societal factors that influenced Rome's development over centuries, before discussing how modern society's shifting attitudes towards renewable energy are accelerating the expansion of solar farms.
Numerous social elements interacted in a complex way to shape Rome's historical history. Political, economic, and cultural factors have affected the city's growth and expansion throughout centuries. Rome's standing as one of the most powerful civilizations in antiquity was influenced by its advantageous geographic position as well as its capable military and political leadership.
Numerous sociological variables, such as the growth of trade networks, technological developments in building and infrastructure, urban planning, and the search of conquests for territorial expansion, all had an impact on Rome's development. All of these elements worked together to push Rome's expansion from a tiny town to a sizable empire that at the time ruled over most of the known globe.
In contrast, perceptions regarding renewable energy sources—particularly solar power—are significantly changing in today's culture. Global interest in shifting to sustainable energy solutions has grown as a result of growing worries about climate change, environmental difficulties, and solar technological advancements.❗️
This change in perspective is hastening the global spread of solar farms. Communities, corporations, and governments are embracing solar energy as a vital part of their efforts to switch to cleaner, more sustainable energy sources and lower carbon emissions. Solar technology is becoming a more appealing alternative for supplying electricity for both smaller-scale residential and commercial uses as well as larger utility projects due to its improving efficiency and affordability.
In light of the growing societal emphasis on sustainability and environmental awareness, the quick rise of solar farms is evidence that contemporary mindsets may bring about real change in a comparatively short amount of time. Similar to how various social factors influenced Rome's development over ages, we are seeing in the modern world how coordinated efforts towards renewable energy can quickly change environments and reshape how we produce energy.
7. Consideration of how Rome's infrastructure continues to inspire city planning and architecture, segueing into a discussion about how modern solar farms may influence future technological advancements.
There is no denying Rome's impact on urban design and architecture. Its magnificent infrastructure still serves as an inspiration for global urban planning and building techniques. Rome's legacy, which includes its aqueducts, roadways, and colossal structures, has had a lasting influence on how we plan and construct cities.
The careful engineering and planning that went into building Rome's infrastructure are still relevant today. Thoughtful design ideas used by Roman engineers can teach us a lot as we battle with sustainability and efficiency concerns in modern cities. In addition to fostering the city's expansion, their capacity to use natural resources like sunshine and water as a resource model still applies to modern sustainable urban development.
Parallel to this, contemporary solar farms mark a significant advancement in the use of renewable energy sources. Similar to Rome's infrastructure, these solar farms are outstanding examples of thoughtful design and ingenuity to meet modern difficulties. Solar farms are helping to create a more sustainable energy future by using large areas of land to collect sunlight and turn it into electricity.
It is evident that the lessons learned from ancient history can impact modern technical achievements when we take into account how Rome's legacy continues to influence our approach to city planning and architecture. One major step toward lowering our dependency on non-renewable resources and creating a more robust infrastructure for the future is the incorporation of solar farms into our energy landscape. Similar to how Rome was not constructed overnight but rather through careful design and ingenuity, solar farms demonstrate the swift pace of advancement that may occur when we look to the past for guidance while simultaneously anticipating the future.
8. Reflection on significant struggles faced during Rome's construction phases paired with present-day challenges encountered when planning, financing, and building solar farms around the world.
Rome's development was an enormous undertaking that took centuries and encountered many difficulties, such as resource shortages and unstable political environments. In a similar vein, modern solar farm construction comes with its own set of difficulties. Conflicting regulations and bureaucratic red tape can make planning and permitting difficult, and financing frequently necessitates navigating challenging investment environments. Overcoming technical obstacles like acquiring land, connecting to the grid, and acquiring the required knowledge are all part of building these solar farms. By thinking back on the difficulties encountered during the building of Rome, we can make comparisons between the difficulties that arise today when building solar farms across the globe.
The intricate process of establishing solar farms now is similar to the difficulties encountered in constructing Rome's monumental buildings. Rome's engineers and architects had to deal with a lack of funding, advanced technology, and complex logistics—all issues that are relevant to contemporary renewable energy initiatives. The inventiveness and tenacity exhibited in antiquity provide motivation for modern attempts to surmount obstacles in the development of solar farms.
The ambitious scope of both the solar farm and Rome construction projects highlights the tenacity needed to successfully traverse difficult planning procedures, obtain funding, and carry out builds. Building solar farms requires perseverance, strategic planning, and a coordinated effort to overcome challenges at every stage of development, much as Rome wasn't built in a day. There are similarities between Rome's historical legacy and the potential long-term effects of broad solar energy adoption, even with the contrasts in time and place.
By looking back at history, we can extract important lessons that still apply today. Understanding how ancient societies overcame hardships to complete massive building projects gives us insights into resilience that we can use to address current issues with renewable energy programs. Gaining insight from past struggles enables contemporary players to tackle obstacles that arise throughout the planning, funding, and construction of solar farms worldwide.
As I mentioned earlier, understanding the complex difficulties Rome faced during its building phases highlights how similar the problems facing the world today are in building solar farm infrastructure. Through historical reflection and current challenges, we may use the collective knowledge from both periods to advance sustainable energy solutions in the face of hardship.
9. Analyze Rome's economic growth through trade networks versus the economic potential unleashed by widespread adoption of solar energy as a result of large-scale solar farm projects.
Rome's extensive Mediterranean trade networks played a major role in the city's economic expansion. Prosperity and progress resulted from the flow of goods, ideas, and culture made possible by the empire's vast network. Rome was able to obtain important resources and promote economic interdependence with other regions thanks to this complex network of trading channels.
On the other hand, large-scale solar farm projects that enable the broad use of solar energy offer a contemporary means of realizing economic potential. Large-scale renewable energy harvesting from solar farms can lessen reliance on non-renewable resources and lessen environmental effect. The expansion of the solar energy industry has the potential to create new jobs, encourage technological advancement, and advance energy independence.
It is possible to draw comparisons between the transformative effects of solar farms and Rome's economic rise through trade networks. Better living standards and steady economic growth are possible outcomes of any scenario. Though Rome's commerce networks thrived for ages, contemporary developments in solar technology have the power to drastically alter economies and quickly implement sustainable energy practices.
The transition to the mass use of solar energy could be a historical turning point comparable to the enormous influence of Rome's trade networks. Adopting and funding solar farms is a strategic move with big economic ramifications in addition to being an environmentally responsible one. Upon examining these two models of economic expansion, it is apparent that although Rome was not constructed overnight, solar farms has the capacity to drastically alter our planet in an exceptionally brief amount of time.
10. Contrast between historical resource management practices in Ancient Rome with sustainable resource utilization methods employed in operating and maintaining large-scale solar farms.
The use of natural resources including land, water, and lumber for the construction of infrastructure was a major component of Ancient Rome's historical resource management techniques. The Romans were well-known for their widespread use of aqueducts, roads, and structures, all of which needed substantial resources to construct and maintain. Nevertheless, the resource management techniques used at the time were not sustainable, which eventually caused environmental damage and the depletion of natural resources.
Large-scale solar farms of today, on the other hand, are planned with sustainability in mind. These solar farms use concentrated solar power systems or photovoltaic panels to capture solar energy and produce electricity. Solar farms use renewable energy sources to minimize their environmental impact, in contrast to the resource-intensive methods used in ancient Rome. In order to ensure that solar farms can produce clean electricity for longer periods of time without depleting natural resources or harming the environment, modern resource utilization strategies prioritize longevity and efficiency.
Large-scale solar farm maintenance is very different from the historical resource management techniques used in Ancient Rome. When solar farms are operating, they require less ongoing resource consumption than ancient infrastructure, which required constant maintenance utilizing a range of natural resources, such as water for sanitation systems or lumber for repairs. To guarantee optimal operation, maintenance procedures mostly involve cleaning panels and doing routine inspections. This low resource requirement is consistent with sustainable methods, which try to minimize their negative effects on the environment while optimizing energy production.
To sum up what I said above, the comparison between the sustainable techniques used in large-scale solar farm operations and maintenance and the historical resource management practices of Ancient Rome shows how technological advancements and a move toward renewable energy have made it possible to use resources in a more environmentally friendly manner. We can minimize our impact on the environment and natural resources while adopting sustainable solutions like solar energy and learning from the past to create a more sustainable tomorrow.
11. Investigation into how lessons from Rome's rise and fall can inform decisions related to long-term planning for sustainable energy solutions like solar farms post-construction phase.
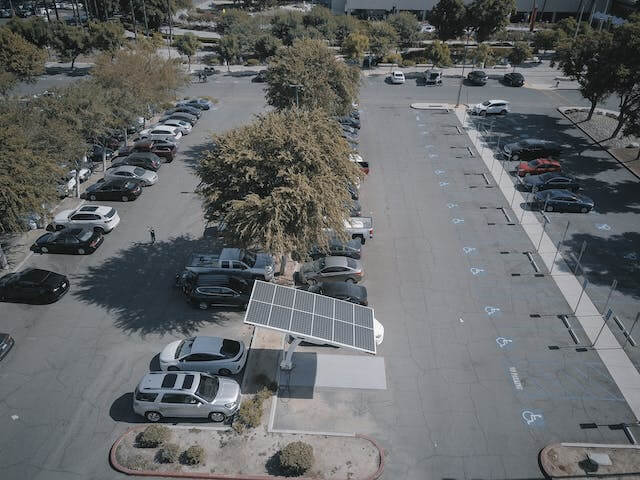

Planning for sustainable energy solutions, such as solar farms, can benefit greatly from an understanding of the rise and fall of Rome. Just as Rome's empire wasn't created overnight, neither can sustainable energy sources. But just as the builders of Rome had to plan ahead, so too do we need to think about solar farms when construction is complete.
We may learn about the significance of long-term planning and maintenance for sustainable energy infrastructure by looking at the lessons learned from the history of Rome. Just like Rome's roads and aqueducts needed constant upkeep to remain operational, solar farms also need on-going maintenance after construction to guarantee their efficacy.
Comprehending the interdependence of environmental, economic, and social elements that played a role in Rome's downfall might offer significant direction for executing efficacious, long-term tactics for upholding and enhancing solar farms. We can make wise decisions on the sustainability and long-term planning of solar energy solutions by using lessons from the past.
Based on the aforementioned analysis, it can be inferred that comparing the development and upkeep of solar farms to the rise and fall of Rome offers insightful information that should be considered when creating long-term plans for sustainable energy sources. Acknowledging the significance of ongoing upkeep and modification after building is essential to guaranteeing the durability and efficiency of solar farms in the contemporary day.
12. Conclusion that ties together insights from both ancient Roman construction processes and contemporary trends in renewable energy development while providing prospects for further innovation in solar farm construction techniques.
Taking into account everything mentioned above, we can claim that the proverb "Rome wasn't built in a day" is meant to serve as a reminder of the time and effort needed to accomplish great things. On the other hand, advancement in the field of solar farms has advanced surprisingly quickly. Modern trends in renewable energy production have driven solar farm construction to new heights, taking inspiration from the inventiveness and tenacity of ancient Roman construction methods.
There are a lot of exciting opportunities for more innovation in solar farm construction methods in the future. As materials science and engineering progress, more economical and efficient ways to build and run solar farms may become possible. By improving overall performance and streamlining operations, integrating robotics and smart technology into the building process has the potential to transform the sector.
Architects, engineers, and environmental specialists working together can create visually beautiful solutions that maximize energy output while blending in with the surrounding terrain. We may continue to build on the foundations left by our ancestors to achieve a sustainable energy future powered by solar farms by utilizing historical lessons and adopting cutting-edge technologies.