1. Introduction:

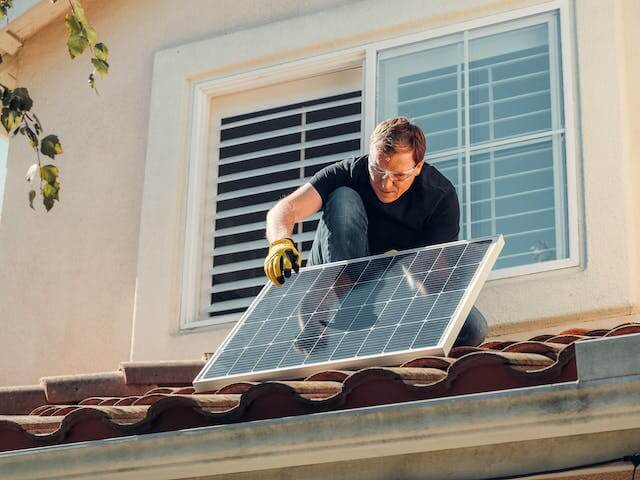
With more than 21% of homes having solar panels, Australia has been one of the world's top users of solar energy. The nation is ideally situated for solar energy due to its plentiful sunshine and pro-solar policies from the government. Globally, concerns over climate change and environmental sustainability are leading to an increase in interest in renewable energy sources. The Australian solar power market is likewise positioned for expansion and innovation in keeping with this trend.
2.
Numerous nations have achieved notable advancements in solar power technologies in the last few years. To increase solar panel efficiency and lower manufacturing costs, nations like China, Germany, and the US have made significant investments in R&D. Australia has been actively involved in global partnerships concerning renewable energy and is keeping a careful eye on these advancements in order to incorporate them into its own infrastructure.
3.
The Australian solar power industry has bright futures, but it also faces obstacles including shifting government regulations and problems with grid integration. Aside from that, certain homes and companies may find the upfront expenditures of installation to be prohibitive. However, as the business develops, chances to solve these issues will arise thanks to continuing technical developments and encouraging federal and state laws.
4.
Australia's solar power sector is predicted to grow significantly by 2024 thanks to rising investment and technological advancement. This expansion will improve economic development and lead to a cleaner environment in addition to generating new job possibilities. In light of the growing worldwide emphasis on sustainability and renewable energy, Australia is expected to persist in augmenting its solar power capacity and adopting novel approaches to community-based energy generation.
5.
From the above, we can conclude that Australia's solar power sector has a lot of exciting prospects because of its prominent role in the global transition to renewable energy. Australia can move toward a more sustainable future driven by clean energy by tackling home issues and learning from global advancements.
2. Overview of International Solar Power Trends:

Leading nations like China, the US, and India have advanced the development and application of solar power technology significantly in recent years. For example, China is investing extensively in large-scale solar projects and has become the world's largest producer of solar panels. The solar capacity of the United areas has been steadily increasing, particularly in areas like Texas and California. India has set lofty goals for the generation of renewable energy and has made impressive strides in the adoption of solar energy.
Australia's own solar business is probably going to be significantly impacted by these global developments in solar power. Australia is ideally suited to large-scale solar power generation due to its plentiful sunshine and expansive landscapes. Australia may maximize its own solar power sector by implementing comparable technologies, legislation, and business models by studying the innovations and best practices in leading worldwide markets. International partnerships and collaborations can also help with information sharing and technology exchange, which could improve Australia's renewable energy environment.✌️
In order to maximize efficiency, price, and environmental impact, Australia must coordinate its solar power activities with international trends in light of the growing global emphasis on sustainability and clean energy. Accepting ideas from international markets can help Australia advance to the forefront of the worldwide transition to renewable energy sources.
3. Government Policies and Incentives:
The world is still moving more and more toward renewable energy sources in 2024. Government regulations and incentives have been put in place in numerous nations to encourage the use of solar energy. For example, the European Union is pushing for carbon neutrality by 2050, and several member states have implemented feed-in tariffs, tax credits, and subsidies to encourage the use of solar energy. Solar adoption in the US has been significantly influenced by federal tax incentives and refunds at the federal and state levels.📧
Australia, on the other hand, has come under fire for having somewhat erratic renewable energy policy. While some states, such as Victoria and South Australia, have made progress with their own efforts, there isn't a single national policy that might provide consumers and businesses thinking about investing in solar energy clarity and uniformity. In comparison to other industrialized countries, a delayed adoption of solar electricity could result from this policy discrepancy.
While the Australian government has experimented with programs like the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES) and the Renewable Energy Target (RET), there are still gaps in long-term planning and coordinated support among all states and territories. This could result in lost chances for economic expansion through the decrease of carbon emissions, innovation, and the creation of jobs.
Australia must seriously explore bringing its solar energy regulations more closely in line with successful foreign models as we move into 2024. Unifying national government initiatives might unleash enormous solar power generating potential, advancing sustainability significantly and stimulating the economy through investments and job growth in the renewable energy industry.
4. Technological Advancements:
Significant technical developments in the solar sector over the past several years have the potential to completely change how we use solar energy. The creation of next-generation solar panels with improved efficiency and less production costs is one of the most revolutionary inventions. Globally, businesses have been devoting resources to research and development in order to produce solar panels that are incredibly thin, flexible, and even transparent, and that can be easily incorporated into a variety of surfaces.
There has been a notable advancement in energy storage technologies. Better solar power storage options have been made possible by advancements in battery technology, such as the widespread use of lithium-ion batteries and the creation of new chemistries. This means that one of the main issues with solar power can be resolved: extra energy produced throughout the day can be stored and used when there is little sunlight or a lot of demand.
By optimizing sunshine exposure and improving overall system performance, advancements in solar tracking systems and smart inverters have maximized the efficiency of solar installations. These developments boost the output of electricity while also enhancing the stability and dependability of solar power systems.
Now, the question is, will Australia adopt these technological advancements? It appears that the response is a resounding yes. With its abundance of sunshine and dedication to renewable energy, Australia's solar industry is expected to benefit greatly from these advancements. To further improve Australia's solar capabilities, research institutes and industry participants there are actively testing and putting these state-of-the-art technology into practice.
The integration of sophisticated solar technologies into Australia's energy landscape is anticipated to be facilitated by government efforts targeted at supporting innovation in renewable energy. Australia is well-positioned to welcome these advancements in its pursuit of a more sustainable future, thanks to laws that encourage the use of clean energy and incentives for research and development.📚
All things considered, it is more likely than not that Australia will not only follow the lead from abroad but also become a leader in implementing these innovations to strengthen its position as a global leader in renewable energy as global advancements in solar technology continue to drive down costs and improve efficiencies.
5. Investment and Funding:
The global focus on shifting to sustainable energy sources has resulted in an increase in international investments in solar installations in recent years. Leading nations have been setting the standard for investment in large-scale solar projects, including China, the US, and numerous European nations. In addition to accelerating technological development, these expenditures have drastically lowered the price of producing solar energy.
Increased foreign investment is expected to be beneficial for Australia's solar industry. Australia offers a compelling potential for international investors due to its massive land area suited for large-scale solar farms and its abundance of sunlight. The nation's attractiveness to international investors in solar projects is further enhanced by its aggressive ambitions for renewable energy and its pro-business policies.
There is a great deal of room for growth in the solar business in Australia. Australia is expected to see an increase in foreign finance as solar power generation costs come down and technology advances. This could result in the creation of more affordable and effective solar infrastructure nationwide, enhancing the sustainability and diversification of the nation's energy supply.
As the world's interest in renewable energy and environmental sustainability grows, Australian solar projects will probably catch the eye of foreign investors looking for chances to fit into their green investment portfolios. Australia now has a great opportunity to take advantage of international investments and grow its solar industry to new heights by 2024 and beyond.
6. Environmental Impact and Sustainability:
International efforts to encourage sustainable solar power techniques are stepping up as the world fights the effects of climate change. Countries all around the world are actively seeking sustainable energy solutions, from large-scale solar project execution to research and development of cutting-edge solar technologies. The goal of collaborative agreements between states and initiatives like the International Solar Alliance is to minimize the environmental impact of solar power while accelerating its adoption.
On the other hand, Australia, with its enormous solar potential, has come under fire for its reliance on fossil fuels and its sluggish adoption of renewable energy sources. Recent events, however, suggest that things may be moving in the direction of sustainability. A growing understanding of the significance of sustainable energy practices is demonstrated by the Australian government's commitment to setting carbon reduction targets and investing in renewable energy infrastructure. With a growing emphasis on sustainability and the effects on the environment, Australia might be well-positioned to coordinate with global initiatives and take advantage of its plentiful solar resources for a more environmentally friendly future.💭
Nations are working together to give priority to sustainable solar power alternatives as awareness of climate change rises worldwide. In an effort to achieve long-term sustainability, international partnerships, research projects, and policy frameworks attempt to promote ecologically friendly practices in the solar business. These initiatives act as a model for nations such as Australia to take into account when formulating their own plans for incorporating solar energy into their energy mix while putting environmental conservation first.
Potential changes in Australia's direction towards sustainability are a reaction to growing stakeholder pressure for more environmental accountability. Reevaluating Australia's approach to solar power generation is becoming more and more popular as a result of growing public knowledge of and lobbying for clean energy sources. This entails providing incentives for the construction of renewable infrastructure, revising legal frameworks, and putting policies into place to lower carbon emissions by putting more solar energy into the grid. Australia can play a key role in promoting sustainable solar power techniques on both a national and global level by understanding the importance of addressing climate change and taking inspiration from activities being undertaken abroad.
7. Challenges and Limitations:

Some recurring obstacles in the development and application of solar technologies have emerged as nations adopt solar power as a sustainable energy source. The erratic nature of solar energy, which depends on sunshine availability and weather, is one of the main problems. This may cause variations in the amount of energy produced, necessitating the use of efficient storage options to guarantee a steady supply of electricity.
The initial expense of solar infrastructure and equipment is another difficulty. Despite the substantial long-term advantages, many nations may find the initial outlay prohibitive. Incorporating solar energy into current electricity systems can also provide logistical and technical challenges. Careful planning and investments in grid modernization are necessary to maintain grid stability while balancing supply and demand.
Development of solar electricity is also hampered by legislative and regulatory restrictions. Government laws that are ambiguous or inconsistent can cause investors and developers to become uneasy, which will impede the growth of this industry. A lack of supportive regulations and restricted access to financing could prevent solar technology from being widely adopted.
These difficulties could hinder Australia's progress in developing solar electricity. The variability of sunshine caused by varying regional weather patterns might impact the dependability of solar energy production. To provide a steady supply of power, addressing this fluctuation will require sophisticated grid management technologies and strong storage options.
Australia's progress towards increasing its solar capacity may be impeded by the upfront expenses associated with setting up solar infrastructure. But these expenses should eventually go down due to economies of scale and ongoing technical developments.
In Australia, the renewable energy industry has also been plagued by policy uncertainty. To get beyond regulatory obstacles and draw in the private sector, it will be essential to have clear, consistent policies that encourage long-term solar power investment.
Australia has enormous potential for solar electricity despite these obstacles because of its plentiful sunshine resources and big open expanses that are ideal for large-scale solar systems. Through the use of technology advancements and knowledge from other regions, Australia may effectively manage these hurdles and achieve notable progress in its transition to solar energy.
8. Public Awareness and Outreach:
International efforts raising public awareness of solar energy have established a standard for growing public support as the demand for renewable energy rises. Creative approaches have been used in nations like the US and Germany to increase public knowledge of the advantages of solar energy. To debunk myths and misconceptions about solar energy, these initiatives include multimedia advertising, community outreach programs, and instructional initiatives in schools.
Australia can effectively boost public support by taking inspiration from these international efforts. Through the use of comparable tactics, such focused educational programs and captivating narratives across diverse media channels, Australia may instruct its populace on the ecological benefits, economic benefits, and comprehensive influence of solar energy. Cultivating collaborations with nearby communities and significant stakeholders will be imperative in establishing a broad comprehension of the importance of shifting to solar power.
Successful overseas campaigns can be used into Australia's outreach programs to raise public awareness and win support for national solar power initiatives. By encouraging the widespread adoption of clean energy techniques throughout Australian communities, this method holds promise for influencing the development of a more sustainable future.
9. Industry Partnerships and Collaboration:

Industry alliances and partnerships are essential for promoting innovation and advancement in the solar power sector. Looking ahead to 2024, it is critical to assess the current partnerships between foreign corporations and domestic organizations in the solar energy industry. These collaborations frequently bring together a variety of skills, resources, and technologies that are crucial to improving Australia's solar energy environment.
International businesses have been collaborating with Australian organizations to introduce state-of-the-art solar technologies and best practices to Australia. These partnerships have made it easier to share expertise, develop technology, and carry out projects on a bigger scale. They have made it possible for regional businesses to enter foreign markets and become significant players in the world solar market.
Based on worldwide patterns, we can forecast possible collaborations in Australia for the year 2024. The drive for sustainable energy solutions is encouraging international cooperation with the goal of improving the infrastructure for renewable energy. Australian businesses are expected to partner with foreign companies that specialize in solar power generation, energy storage solutions, grid integration technology, and creative financing methods, as the global focus on decarbonization and the shift to renewable energy intensifies.
Worldwide patterns suggest an increasing focus on comprehensive strategies for sustainability that cover the production, distribution, storage, and use of renewable energy. This suggests that Australian organizations may collaborate with foreign businesses that provide all-inclusive solutions for incorporating solar energy into larger energy ecosystems. As Australia aligns its solar endeavors with global breakthroughs, collaboration in areas like demand-side management, microgrid deployment, and smart grid development may become commonplace.
The need to address climate change and become carbon neutral also creates opportunities for joint ventures centered around large-scale solar systems with integrated storage. Foreign enterprises possessing vast expertise in creating utility-scale solar farms integrated with cutting-edge energy storage systems could potentially form strategic alliances with Australian utilities or developers seeking to enhance the country's renewable energy portfolio.
Considering how Australia's solar power business is expected to develop in 2024 and beyond, it is critical to look at successful global partnerships in order to spot potential local alliances. Australian stakeholders may strategically position themselves to fully embrace the potential of solar power through impactful industrial alliances by harnessing global trends and insights from international experiences. 😄
10. Regulatory Frameworks and Standardization:
Australia's solar energy market is expected to follow international trends in 2024, especially with regard to standardization and regulatory frameworks. Examining international laws governing the use of solar power is essential as the nation seeks to increase its solar energy potential. Australian legislators and industry stakeholders may learn a great deal about best practices and potential pitfalls by closely examining the regulatory frameworks of leading solar markets like Germany and the US.
It is imperative to consider the potential effects of standardization initiatives on the Australian market in order to guarantee the smooth integration of solar power technology. Global advances in energy storage, grid integration, and solar panel efficiency mean that keeping Australia's standards in line with international norms will be essential to promoting innovation and industry interoperability. Through assimilating global standardizing experiences, Australia may establish itself as a frontrunner in the adoption of sustainable energy technologies.
Australia can steer its solar power industry towards a sustainable, competitive, and reliable path by utilizing the knowledge gained from international regulatory frameworks and standardization activities. A prosperous solar power landscape for years to come will be shaped by blending global insights into local policy development as the country continues to embrace renewable energy sources.
11. Case Studies from Abroad:
Australia has frequently looked to global solar power initiatives for leadership and inspiration. Successful solar projects around the world, from the Middle East's deserts to Europe's busy cities, have provided important insights for Australia's own energy transformation. One such example is the Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park in Dubai, which has set high goals for producing renewable energy and has been successful in utilizing the desert climate to significantly increase solar potential. This project is a useful lesson for areas of Australia with similar climate circumstances because it shows how creative technology and smart design can result in significant solar energy outputs in arid locations.
Germany's extensive portfolio of rooftop solar installations is another interesting case study. Given that Germany has a population density that is similar to Australia's, studying the country's rooftop solar industry's performance can offer important insights into incorporating solar electricity into urban settings. When trying to encourage widespread adoption of solar energy inside cities and towns, Australian planners should take into account two crucial factors: making optimal use of urban space and offering incentives for residential and commercial solar adoption.
Improvements in battery storage technology should be closely monitored, especially in areas such as California where significant progress has been made in the integration of large-scale battery systems with solar farms. These developments are particularly relevant given Australia's challenges in integrating intermittent renewable energy sources into its extensive system infrastructure. It will be essential to comprehend how abroad projects have effectively incorporated storage solutions into their solar endeavors in order to guarantee stability and dependability inside Australia's changing energy environment.
Through a thorough examination of these international case studies, Australian stakeholders, energy suppliers, and policymakers can acquire useful knowledge for developing resilient and sustainable solar projects that are suited to the nation's distinct geographical and demographic features. Australia will need to take a cue from these global leaders as 2024 approaches in order to successfully navigate its own solar goals.
12. Conclusion:
To summarize the above, we can conclude that there is a lot of room for expansion and innovation in the solar power business based on worldwide trends. As they move toward renewable energy sources, nations all around the world are adopting solar energy more and more. Widespread adoption is being propelled by the falling costs of solar technologies as well as improvements in grid integration and storage solutions.
As Australia continues to increase its capacity for renewable energy, its approach to solar power is probably going to follow international models. Australia's investment in solar power infrastructure is expected to rise due to a combination of factors including government incentives and supporting regulations, combined with the declining costs of solar panels and batteries. But as Australia looks to maximize its solar energy potential while taking certain local issues into account, special geographic and regulatory challenges may potentially cause some deviation from global trends.
Australia's solar power development trajectory seems set to follow worldwide patterns as the nation works to take advantage of its plentiful sunshine and move toward a more sustainable energy future.