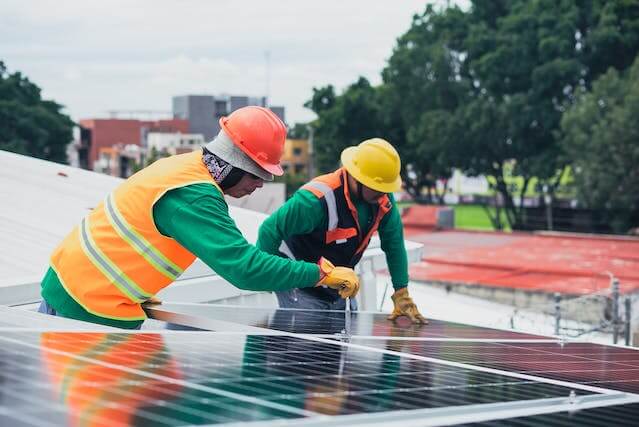
1. Introduction: Exploring the significance of critical minerals in the transition to a net-zero economy. Discussing the unveiling of the critical minerals grants guidelines and its implications for sustainable resource management.

It is impossible to exaggerate the importance of essential minerals in the shift to a net-zero economy. These minerals are necessary for the development of electric cars, renewable energy sources, and other cutting-edge technology. Sustainable extraction and supply of essential minerals have become critical issues as demand rises in tandem with attempts to minimize carbon emissions.
The release of the rules for essential minerals grants has generated a lot of attention lately. These rules are expected to be crucial in forming sustainable resource management procedures, guaranteeing ethical mineral extraction, processing, and recycling. These rules have consequences that go beyond environmental concerns to include economic and geopolitical aspects as countries endeavor to achieve self-sufficiency in this critical area.
This breakthrough is a big step in the right direction toward solving the problems of maintaining a steady supply chain for essential minerals while reducing their negative environmental effects. It emphasizes how these materials' strategic role in creating a more resilient and sustainable future is becoming increasingly recognized.
2. Importance of Critical Minerals: Highlighting the essential role of critical minerals in various industries such as renewable energy, electric vehicles, and technology, emphasizing their importance in achieving net-zero goals.
As the sectors for technology, electric vehicles, and renewable energy continue to grow rapidly, critical minerals will become increasingly important in powering the future. Batteries, magnets, and other vital parts that power the renewable energy revolution cannot be produced without these minerals. Their contribution to the development of environmentally friendly technology and the decrease of greenhouse gas emissions makes them significant. Critical minerals are becoming more important components that support global efforts to achieve net-zero emissions.
Critical minerals are essential to the design and installation of solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems in the field of renewable energy. Minerals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel are essential to the effective operation of technologies like lithium-ion batteries. Similar to this, the battery packs and electric motors of electric vehicles heavily rely on essential minerals. It becomes difficult to make the shift to a low-carbon economy without these vital resources.
Essential minerals are essential to the development and production of electronic gadgets like computers, smartphones, and other high-tech equipment. It is anticipated that as technology advances quickly, so too will the need for these minerals. Thus, maintaining a steady and long-lasting supply chain for essential minerals becomes crucial to driving digital transformation and meeting carbon-neutral goals.
Incorporating key minerals into strategic strategies is imperative as governments throughout the globe pledge to reduce their environmental impact and battle climate change by achieving net-zero emissions targets. The dependence on these minerals emphasizes how important a role they play in accomplishing sustainability objectives in a variety of businesses. Recognizing the significance of maintaining a robust supply chain for essential minerals becomes even more imperative as we get closer to a net-zero future in order to advance a cleaner and more sustainable global community.
3. Overview of Net-Zero Objectives: Discussing the global efforts towards net-zero emissions and how the utilization of critical minerals is pivotal in this endeavor.
The global movement to achieve net-zero emissions has accelerated significantly in the last several years. An increasing number of nations, companies, and organizations have committed to bringing down greenhouse gas emissions to zero by the year 2050. Reaching this lofty objective calls for an all-encompassing strategy that includes advances in energy efficiency, renewable energy technology, and the broad electrification of transportation and other industries.
The growing need for vital minerals is a crucial part of the shift to a low-carbon economy. These minerals, which include lithium, cobalt, rare earth elements, and others, are necessary for the manufacturing of sustainable energy systems including solar panels, wind turbines, and batteries for electric vehicles. Critical minerals are in increasing demand worldwide, and this demand is driving up the need for a sustainable and ethical supply of these minerals.
Using key minerals is essential to the effort to achieve net-zero emissions. A steady and safe supply of these minerals is necessary to avoid major obstacles on the path of the low-carbon economy. Therefore, in order to support the global endeavor to achieve net-zero emissions, systems that ensure the responsible extraction, processing, and recycling of important minerals must be developed. In order to move closer to a sustainable energy future, it is imperative that efforts in vital mineral supply chains to guarantee social responsibility and reduce environmental effect be made.
4. Critical Minerals Grants Guidelines: Providing an overview of the newly released guidelines, outlining key eligibility criteria and application process for grants targeting critical mineral projects.
The recently published vital Minerals Grants Guidelines are an important step toward assisting initiatives that seek to solve the issues surrounding vital minerals in order to help achieve net-zero goals. For interested parties looking to raise money for their projects, the guidelines offer a clear structure.
The rules contain important eligibility requirements that specify the kinds of projects that are eligible for funding. The emphasis on extracting, refining, or recycling key minerals, as well as the possible influence on lowering supply chain vulnerabilities and boosting domestic production capacities, are a few examples of these criteria.
To make everything clear and transparent for prospective candidates, the application procedure for these funds has been thoroughly described. Deadlines for submissions, necessary paperwork, evaluation standards, and reporting and monitoring requirements could all be part of this process.
By providing this summary of the rules, interested parties can learn crucial information about how to secure funding for initiatives that support net-zero initiatives overall and strengthen sustainable key mineral practices.
5. Addressing Sustainability Challenges: Exploring how the guidelines aim to prioritize environmental sustainability and responsible mining practices within critical mineral production.
A big step in the right direction toward solving sustainability issues in the mining sector is the recently issued critical minerals award guidelines. The recommendations are designed to encourage the production of key minerals in an ethical and environmentally responsible manner by giving priority to environmental sustainability and responsible mining practices.
Encouraging mining operations to reduce their environmental impact is one of the main goals of the standards. This entails putting policies into place to lessen habitat destruction, manage water better, and cut down on carbon emissions. The guidelines stress the significance of implementing resource efficiency and waste reduction as top priorities for implementing sustainable mining technologies and practices.
The recommendations emphasize responsible mining methods in addition to environmental issues. This means advocating for moral work practices, community involvement, and supply chain transparency. The rules aim to ensure that mining operations respect labor norms and human rights while benefiting local communities by incorporating these concepts into vital mineral production.
It is clear that the guidelines represent a proactive approach towards achieving net-zero emissions and fostering sustainable development in the critical minerals sector by examining how they prioritize environmental sustainability and responsible mining practices within the production of critical minerals.
6. Economic and Geopolitical Implications: Examining the economic and geopolitical significance of securing a stable supply chain for critical minerals as countries strive to meet their net-zero commitments.

As nations work to meet their net-zero obligations, maintaining a secure supply chain for essential minerals has important geopolitical and economic ramifications. Electric cars, renewable energy technologies, and other low-carbon technologies depend on critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements. As the world's need for these minerals keeps growing, it is imperative to guarantee a steady and sustainable supply in order to facilitate the energy transition.
Economically speaking, minimizing reliance on a small number of producing nations and averting possible supply chain interruptions that can impede the switch to clean energy depend on maintaining a steady supply of essential minerals. In the end, diversifying the sources of essential minerals can assist the economic viability of implementing green technologies by enhancing market stability and lowering price volatility.
In terms of geopolitics, nations vying for control over vital resources have turned it into a point of strategic rivalry as they try to solidify their positions in the developing low-carbon economy. Global power dynamics and geopolitical dynamics can be shaped by the control of resources such as lithium and rare earth elements. The risks connected with mineral extraction for the environment and society can be reduced by working to develop more moral and sustainable mining practices.
In order to encourage responsible sourcing practices and get closer to net-zero goals, countries must adopt transparent rules for vital mineral grants while they manage these geopolitical and economic hurdles. Policymakers may contribute to ensuring a dependable supply chain that supports both economic growth and environmental stewardship by promoting international collaboration and supporting investments in sustainable mining initiatives.
7. Technology and Innovation: Highlighting potential technological advancements and innovative solutions that could emerge from investments in critical mineral projects supported by these grants.

To achieve net-zero emissions, the publication of the Critical Minerals Grants Guidelines is an essential step. The emphasis on technology and innovation is one of the most important features since it draws attention to the possibility that investments in important mining projects funded by these grants could result in significant technical breakthroughs and creative solutions.
Critical mineral project investments could spur technical breakthroughs that transform a range of sectors. Critical minerals are essential to the development of emerging technologies including electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and sophisticated battery storage. Grants allocated to these projects might therefore hasten the creation and commercialization of novel solutions in these fields.
Grants supporting important mining initiatives might encourage industrial participants and research institutes to work together. These kinds of partnerships are crucial for fostering creativity and identifying fresh approaches to the sustainable extraction, processing, and recycling of vital minerals. The recommendations provide up a channel for the development of an ecosystem that would eventually support the advancement of technological innovations and a more sustainable future.
As I mentioned earlier, the Critical Minerals Grants Guidelines' emphasis on innovation and technology has great potential to advance the goal of net-zero emissions. Through showcasing the technological advances and creative solutions that could result from funding vital mineral projects that these funds enable, a clear road ahead for utilizing these resources to speed up sustainable developments across multiple industries is provided.
8. Impact on Renewable Energy Sector: Analyzing how access to critical minerals through these grants could accelerate the growth of the renewable energy sector, contributing to a cleaner, more sustainable energy mix.

A big step has been taken in the direction of quickening access to vital minerals, which are necessary for the expansion of the renewable energy industry, with the publication of the Critical Minerals Grants Guidelines. These grants have the potential to have a significant influence on renewable energy systems by offering advice on procuring essential minerals.
For the manufacturing of renewable energy components like solar panels, wind turbines, and batteries, access to essential minerals is essential. A cleaner and more sustainable energy mix can be achieved and the growth of renewable energy infrastructure can be accelerated by the availability of these minerals through the grant program. This is in line with international initiatives to switch to renewable energy sources in order to cut carbon emissions and fight climate change.
These incentives could improve energy security and independence by making vital minerals more accessible for renewable energy technology. A more resilient and diverse energy landscape may result from a decrease in the use of conventional fossil fuels and an increase in the use of clean energy sources.
To encapsulate my earlier writing, these incentives have a significant impact on the renewable energy industry. The development of renewable energy technologies is accelerated by access to essential minerals, which eventually leads to the development of an energy ecosystem that is more ecologically friendly and sustainable. The published standards represent a significant step toward reaching net-zero aims and promoting a more environmentally friendly future driven by readily available and clean energy sources.
9. Stakeholder Engagement: Discussing opportunities for collaboration between government, industry, and local communities in advancing responsible extraction and processing of critical minerals.
In order to advance responsible mineral extraction and processing and reach net-zero targets, stakeholder engagement is crucial. Government, business, and community cooperation offers many chances to address social and environmental issues while advancing sustainable practices.
The establishment of laws and policies governing the mining and processing of vital minerals is mostly the responsibility of government organizations. Governments may guarantee that mining operations are carried out in an environmentally friendly manner while also taking into account the social impacts on neighboring communities by interacting with industry stakeholders and local populations.
In order to promote technological innovation and best practices for sustainable mineral extraction and processing, industry cooperation is essential. While intimate collaboration with local communities can build trust, transparency, and mutual benefit, industry collaboration with government organizations can assist industries align their operations with regulatory standards.
Since mining operations have a direct influence on local people, ensuring responsible mineral extraction depends heavily on their involvement. Working together with local stakeholders makes it possible to incorporate community needs and traditional knowledge into mining projects, resulting in more inclusive and sustainable outcomes.
Based on the aforementioned, it can be inferred that involving stakeholders provides a forum for cooperative endeavors aimed at promoting ethical extraction and handling of vital minerals. It is feasible to promote significant advancement while striking a balance between social progress, economic development, and environmental preservation by establishing alliances between the public sector, business, and local communities.
10. Global Collaboration for Sustainable Resource Management: Emphasizing the need for international cooperation and sharing best practices in managing critical mineral resources sustainably towards achieving global net-zero targets.
In order to achieve the global net-zero targets, it is imperative to highlight the necessity of international cooperation and to share best practices in the sustainable management of vital natural resources. Crucial minerals like lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements are predicted to become more in demand as nations work to lessen their carbon footprint and switch to renewable energy sources. In order to guarantee the ethical extraction, processing, and recycling of these vital resources, cooperation between nations is required.
In order to meet the increased demand for vital minerals while reducing environmental damage, global collaboration for sustainable resource management will be essential. Countries can create creative solutions for ethical mining methods, effective mineral processing procedures, and circular economy projects that support recycling and reusing these priceless minerals by exchanging best practices and utilizing one another's experience.
Cooperation between nations can help spread information about finding new sources of essential minerals, strengthening supply chain security, and creating substitute materials to reduce reliance on finite resources. Countries can work together to diversify sources of essential minerals and accelerate the development of cutting-edge technologies that are less dependent on these finite resources by forming partnerships and conducting cooperative research.
Prioritizing international cooperation for sustainable resource management is, in essence, essential to achieving a future in which vital mineral supply chains are resilient, socially and environmentally responsible, and ecologically sound enough to facilitate the shift to a net-zero carbon economy.
11. Ensuring Fair Access and Distribution: Delving into strategies outlined in the guidelines to ensure fair access to critical minerals grants while addressing distribution challenges to support equitable development across diverse industries.
In order to promote equitable growth across a range of industries, the criteria for key minerals awards place a strong emphasis on the necessity of guaranteeing fair access and distribution. The recommendations explore techniques that tackle distribution issues in order to do this. They hope to achieve this by leveling the playing field and giving all parties involved equal chances to obtain grants for vital minerals.
Transparency and inclusion in the grant application and allocation procedure are essential elements delineated in the rules. This entails defining precise standards for assessment and eligibility in addition to actively involving a wide variety of stakeholders in the decision-making process. The recommendations aim to eliminate potential biases or hurdles that may impede equitable access to funds for key minerals by promoting openness and inclusivity.
The guidelines stress how crucial it is to take industry-specific requirements and geographical differences into account when distributing funding. They provide a customized strategy that takes into consideration the disparities in infrastructure, knowledge, and market demand among various areas and sectors. The goal is to make sure that vital minerals funds are awarded in a way that promotes equitable development and economic expansion across a range of industries by taking these aspects into account.
Apart from tackling issues related to distribution, the guidelines also underscore the importance of promoting cooperation and exchange of expertise among recipients of grants. They hope to increase the impact of essential minerals funding and foster synergies between grantees from various industries by fostering networking opportunities and information exchange. By working together, we hope to increase the advantages of vital minerals grants and make more significant strides toward sustainable resource management.✍️
In addition to guaranteeing equitable access to vital minerals awards, the techniques defined in the recommendations aim to preemptively tackle distribution difficulties. These principles, which place a strong emphasis on equity, openness, diversity, and cooperation, provide a vital foundation for directing the prudent distribution of resources in the direction of reaching net-zero goals and promoting fair growth across a range of industries.
12. Conclusion - Summarizing the potential impact of these grants guidelines on fostering a sustainable approach to critical mineral extraction, processing, and utilization on our journey towards a net-zero future.

From the foregoing, it is clear that the publication of the critical minerals grants guidelines represents a major advancement toward the development of a sustainable strategy for the extraction, processing, and use of essential minerals. These awards have the potential to significantly speed up our transition to a net-zero future by offering precise direction and assistance for initiatives focused on creating ethical standards in the vital minerals industry.
These funds could have a significant impact since they have the ability to reward creativity and best practices that put social responsibility and environmental stewardship first. These principles can assist in reshaping the vital minerals industry towards a more sustainable trajectory by promoting the development of technologies and techniques that lessen environmental footprint and uphold ethical labor standards.
These funds can help mitigate the environmental effects of crucial mineral extraction while simultaneously fostering economic growth and technological advancement by supporting projects that are in line with net-zero aims and sustainability principles. By doing this, they open the door to a time when the sourcing and use of essential minerals will be done in a way that is respectful to the environment and human society as we work towards reaching net-zero emissions.